Connecting the Real Time Clock
In order to record a timestamp for each data point, a battery-backed real time clock (RTC) is quite useful. The RTC is an I2C device, which means that it uses 2 wires to communicate. Both wires are used to set the time and retrieve it. On the Arduino UNO, these pins are the Analog 4 and 5 pins.
- 5V is used to power to the RTC chip when you want to query it for the time. If there is no 5V signal, the chip goes to sleep using the coin cell for backup.
- Connect GND to common power/data ground
- Connect the SCL pin to the I2C clock SCL pin on your Arduino. On an UNO based Arduino, this is also known as A5, on a Mega it is also known as digital 21 and on a Leonardo/Micro, digital 3
- Connect the SDA pin to the I2C data SDA pin on your Arduino. On an UNO based Arduino, this is also known as A4, on a Mega it is also known as digital 20 and on a Leonardo/Micro, digital 2
These modules are usually equipped with rechargeable 40 mA 3.6 V LIR2032 coin cell batteries. In case you need longer battery life, they can be exchanged with a non-rechargeable 3 V 200 mA coin cell. However, this requires to unsolder a resistor on the board to disable battery-charging when the module is connected to 5 V!
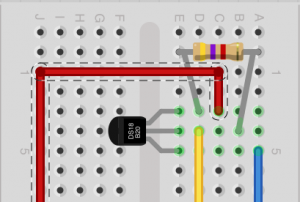
Connecting the Temperature Sensor (DS18S20)
The DS18B20 ‘1-wire’ sensors can be connected in parallel – unlike nearly any other sensor sold! All sensors should share the same pins, but you only need one 4.7K resistor for all of them. The 4.7k pullup resistor is placed between the data (yellow wire) and 5 V pin (red wire) of the sensor. The data pin can be wired to any digital Arduino pin, given that you configure it’s pin number in your sketch.
Wiring a status LED (optional)
In order to keep track of data recording, you can wire a standard 20 mA LED with 220 Ω resistor to the data logger, which briefly flashes to indicate that data are stored on the card.
Arduino Sketch
The sketch below will store each data point on a separate line in a CSV file called ‘datalog.txt’.
Tue;01-11-2016 14:52:29;20.87 Tue;01-11-2016 14:53:01;20.87 Tue;01-11-2016 14:53:32;20.94 Tue;01-11-2016 14:54:03;20.94 Tue;01-11-2016 14:54:34;20.94
If you need a different output format than day-of-week;ISO-date;temperature, you have to modify the show_temperature(), show_time_and_date() and saveData() functions.
Click on ‘show‘ to open the sketch.
Spoiler
// Description SD-Card Temperature Data-Logger
// Author: http://raspberryblog.de
// Date: 2016-10-31
// Version: 1.0
// Depends: 1-Wire Library http://www.pjrc.com/teensy/arduino_libraries/OneWire.zip
// RTC Library https://github.com/jcw/rtclib
// SD-Card Library Build-In
// SPI library Build-In
// ArduinoTemperatureCtrl http://download.milesburton.com/Arduino/MaximTemperature/DallasTemperature_372Beta.zip
//
// RTC:
// SDA: A4
// SCL: A5
// SD-Card:
// MISO: D12
// SCK: D13
// MOSI: D11
// CS: D10
#include <Wire.h> // I2C-Library
#include "RTClib.h" // RTC-Library
#include <SD.h> // SD-Library
#include <SPI.h> // SPI-Library
RTC_DS1307 RTC; // RTC Modul
#include <OneWire.h> // OneWire-Library
#include <DallasTemperature.h> // DS18B20-Library
#define DS18B20_PIN 2 // Data Pin for DS18B20
#define LED_PIN 3
#define INTERVAL 30000 // Read sensor each 30 seconds
OneWire oneWire(DS18B20_PIN); // OneWire
DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire);// DS18B20
const int chipSelect = 10; // CS is Pin D10 on most Arduino Boards i.e. D53 on the Mega, D4 on Ethernet Shield
File dataFile; // create file-handle data logging
void setup(void) {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C Bus
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set LED Pin to OUTPUT mode
RTC.begin(); // Start RTC
Serial.begin(115200); // Enable Serial
Serial.print("Starting Date, Time and Temperature...");
if (! RTC.isrunning()) { // Set RTC time from system time
RTC.adjust(DateTime(__DATE__, __TIME__));
Serial.println("RTC was started and set to system-time!");
}
else Serial.println("RTC already running!");
Serial.print("Initializing SD-Card...");
pinMode(SS, OUTPUT);
if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) {
Serial.print("SD-Card error or card not found!");
while (1) {
ledBlink(); // Stop in endless loop
}
}
Serial.println("SD-Card ready!");
dataFile = SD.open("datalog.txt", FILE_WRITE);
if (! dataFile) {
Serial.println("Error! File: datalog.txt not found!");
while (1) {
ledBlink(); // Stop in endless loop
}
}
sensors.begin(); // Start DS18B20
}
void loop(){
DateTime now=RTC.now(); // Get current time from RTC
show_time_and_date(now); // Print formatted Date and Time
sensors.requestTemperatures(); // ReadTemperature
show_temperature(sensors.getTempCByIndex(0));
saveData(now, sensors.getTempCByIndex(0));
delay(INTERVAL); // Wait 30 seconds
}
String get_day_of_week(uint8_t dow) {
String dows=" ";
switch(dow){
case 0: dows="Sun"; break;
case 1: dows="Mon"; break;
case 2: dows="Tue"; break;
case 3: dows="Wed"; break;
case 4: dows="Thu"; break;
case 5: dows="Fri"; break;
case 6: dows="Sat"; break;
}
return dows;
}
// Format DOW;YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS;
void show_time_and_date(DateTime datetime){
Serial.print(get_day_of_week(datetime.dayOfWeek()));
Serial.print(";");
if(datetime.day()<10)Serial.print(0);
Serial.print(datetime.day(),DEC);
Serial.print("-");
if(datetime.month()<10)Serial.print(0);
Serial.print(datetime.month(),DEC);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.print(datetime.year(),DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
if(datetime.hour()<10)Serial.print(0);
Serial.print(datetime.hour(),DEC);
Serial.print(":");
if(datetime.minute()<10)Serial.print(0);
Serial.print(datetime.minute(),DEC);
Serial.print(":");
if(datetime.second()<10)Serial.print(0);
Serial.print(datetime.second(),DEC);
Serial.print(";");
}
void show_temperature(float temp){
Serial.println(temp);
}
void ledBlink() {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(200);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
}
void saveData(DateTime datetime, float tempC) {
String dataString = "";
dataString += String(get_day_of_week(datetime.dayOfWeek()));
dataString += ";";
dataString += String(datetime.year(),DEC);
dataString += "-";
dataString += String(datetime.month(),DEC);
dataString += "-";
dataString += String(datetime.day(),DEC);
dataString += ";";
dataString += String(datetime.hour(),DEC);
dataString += ":";
dataString += String(datetime.minute(),DEC);
dataString += ":";
dataString += String(datetime.second(),DEC);
dataString += ";";
dataString += String(tempC);
//Serial.println(dataString); // Debug
ledBlink();
dataFile.println(dataString); // Write to SD-Card
ledBlink();
// If you want to speed up the system, remove the call to flush() and it
// will save the file only every 512 bytes - every time a sector on the
// SD card is filled with data.
dataFile.flush();
}