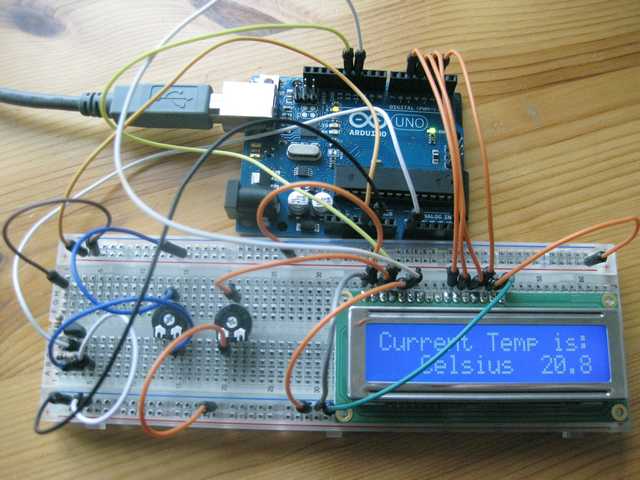
The sketch below was adopted from the Adafruit tutorial for 16×2 LCD displays. Since the LM335Z provides the absolute temperature in degrees Kelvin, temperature values are first converted to Fahrenheit or Celsius before printing them on the display.
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
float tempC = 0;
float tempf = 0;
int tempPin = 0;
float samples[8];
float maxi = 0,mini = 100;
int i;
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
lcd.begin(16, 2);
lcd.setCursor(2, 0);
lcd.print("LM335Z");
lcd.setCursor(3, 1);
lcd.print("Thermometer");
delay(5000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(2, 0);
lcd.print("LCD displays");
lcd.setCursor(1, 1);
lcd.print(" averaged temp ");
delay(5000);
lcd.clear();
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("LM335Z Raw data: ");
Serial.println(analogRead(tempPin));
for(i = 0;i<=7;i++) {
samples[i] = (( 5.0 * analogRead(tempPin) * 100.0) / 1024.0) - 273.15;S
Serial.println(samples[i]);
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Current temp is: ");
lcd.setCursor(1, 1);
lcd.print(" Celsius ");
lcd.setCursor(12, 1);
lcd.print(samples[i]);
tempC = tempC + samples[i];
delay(800);
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("");
tempC = tempC/8.0;
tempf = (tempC * 9)/ 5 + 32;
if(tempC > maxi) {
maxi = tempC; }
if(tempC < mini) {
mini = tempC; }
Serial.println("New measurement:");
Serial.print(" Average Temperature in Celsius is " );
Serial.println(tempC);
Serial.print(" Average Temperature in Fahrenheit is " );
Serial.println(tempf);
Serial.print(" MAX Temperature in Celsius is " );
Serial.println(maxi);
Serial.print(" MIN Temperature in Celsius is " );
Serial.println(mini);
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" Fahrenheit ");
lcd.setCursor(12, 1);
lcd.print(tempf);
delay(5000);
tempC = 0;
}
If you’re done, the display should show the average temperature of 8 measurements, alternating between Celsius and Fahrenheit.